Which Cryptocurrency exchange offer the best condition to buy and hold Ether? Check out hte ranking here today.
The Best Exchanges to buy and invest in Ether
Do you want to buy and sell Ethereum’s Ether (ETH)? Now you are looking for an exchange to invest in Ether tokens?
Check out the 3 best exchanges to invest in Ethereum today.
| Best Exchanges to buy and invest in Ethereum’s Ether (ETH) | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Bybit | Bybit offers stablecoin-margined Options contracts to help you expand trading opportunities, and Portfolio Margin to help you maximize capital efficiency. |
| 2. Binance | The largest Cryptocurrency exchange in the world. Buy, trade, and hold 600+ cryptocurrencies on Binance |
| 3. Huobi | Huobi, a Leading Digital Asset Trading Platform. A wide array of digital asset trading and management services to satisfy diverse trading needs. |
| 4. BitMEX | Supporting more than 30 Cryptocurrencies. Get crypto’s most advanced trading platform on your device. |
Ethereum is a blockchain-based decentralized cryptocurrency platform created by Vitalik Buterin and has the second highest market capitalization after Bitcoin. It has redefined the entire crypto industry since the introduction of smart contracts . To get the best understanding of Ethereum, let’s compare it to Bitcoin.
Ethereum vs Bitcoin
Ethereum and Bitcoinare two projects that are similar in many ways but ultimately have different goals. The first thing they have in common is that both are decentralized systems, with no entity controlling them. Instead, the system operates on a global computer network volunteered by participants called nodes. In other words, both rely on blockchain technology to securely and publicly record data or transactions. Their differences become evident in terms of long-term goals for the technology in question. Bitcoin is the first cryptocurrency or money transfer system recorded on a decentralized public ledger, whereas Ethereum is a versatile platform. It has its own digital currency, Ether (ETH), but this is only one component of the overall system. Ethereum significantly extends Bitcoin’s core technology, providing a network for creating and deploying other decentralized applications (DApps). These applications may be entirely new concepts or new versions of existing concepts. For example, decentralized finance, or DeFi, is one of the most popular fields currently being developed on the Ethereum network, traditional financial services that have been reimagined and reorganized without third-party intermediaries. Imagine being able to borrow or lend money worldwide without any bank or other fees. Furthermore, imagine that all interest and transaction fees generated go directly to the borrower. This is truly a peer-to-peer system, where all interactions occur directly between users. Even if only the cryptocurrency component of Ethereum is compared to Bitcoin, there are still some important differences. The maximum supply of Bitcoin is 21 million. Ether, on the other hand, has no limits. Ethereum also aims to mine blocks on average at an average of 12 seconds per block, much faster than Bitcoin’s 10 minutes. Finally, Bitcoin mining requires far more resources, requiring dedicated, custom machines that few can afford. In comparison, it is much easier for the general public to participate in ETH mining, encouraging more decentralization.
What is a smart contract?
Smart contracts are a new feature introduced by Ethereum, which has catalyzed the development of countless new decentralized applications. Just like a physical contract, it can be understood as a binding contract between two parties. But in reality, signing a contract does not guarantee the promised results. In fact, contracts are always broken or ignored. These paper documents are merely deterrents that depend on the enforcement powers of the laws and government agencies that support them. Smart contracts do not have this weakness. It is represented as computer code that runs exactly as intended on the Ethereum blockchain. Once deployed, it is automated and cannot be censored or tampered with. Facilitate the trade or exchange of money, data, content, or anything of value. Smart contracts work on their own. In other words, your code is designed to execute certain actions when certain conditions are met. Let me explain the effectiveness of smart contracts with a simple example. When you make the assumption that you want to buy an ebook from someone on the other side of the globe, you can put your trust in it. If you send money, how can you guarantee that the seller will actually send the product? Conversely, if the seller sends the book first, there is a risk that the payment will not be received. One solution is a brokerage or trusted escrow service that holds payments and releases them when there is evidence that the product has been shipped. Of course, you will have to pay a fee to the escrow company. But in fact, even under these circumstances, there must be a belief that even the broker will not intercept your money. Using smart contracts on the Ethereum network eliminates all of these problems. A code that automatically sends a copy of the ledger when a specified amount of funds is transferred to the target account is a much more effective solution. No intermediaries other than buyers and sellers are required, no additional fees are charged, and everything happens automatically with a publicly verifiable record of transactions on the blockchain. Developers can leverage these smart contracts to create applications that are more complex than they can imagine. All of these new services will share the characteristics of decentralization, automation and transparency, which That’s what’s happening in the DeFi pandemic. A variety of traditional financial and banking services are being reinvented on the Ethereum network using smart contracts, but there are many other decentralized industries outside of finance. Counting systems, social networks, and even games all have the potential to revolutionize.
Go to Bybit’s Official Website
Disadvantages of ETH
While there are many possibilities in practice, Ethereum’s smart contract functionality has a potentially significant flaw: human error. Non-editable smart contract code is, after all, the same person who wrote it. If you make a mistake or leave an exploitable bug, there are many cases where it can be used maliciously. Once that happens, there’s very little you can do to reverse the damage. Of course, you can write a new and improved version of the contract, but since all transactions that occurred using the old contract have already been recorded and made permanent on the blockchain, there is no other way than to revert the transaction through general consensus and rewrite the underlying code. But this ultimately goes against the core philosophy of the immutable ledger. Whenever such a mistake occurs, trust in the Ethereum network is weakened and the value of ETH is greatly reduced. Nevertheless, this exciting sector is still growing and has so far restored and revived investor confidence several times.
What is Ethereum Gas?
Anyone familiar with Ethereum will know that an ongoing problem with Ethereum is its high transaction fees. This has been going on since the network first experienced congestion in 2017 and 2018. Nevertheless, DeFi applications have seen explosive growth. This also means that, in some cases, only large investors can survive in the market. In the end, fees lead to profits.
In the first week of January 2021, transaction fees hit a new average high of nearly $18 .
Ethereum gas is part of this volatile fee equation. Gas represents the amount of computing power required by Ethereum miners to confirm a transaction. Miners spend computing energy in exchange for mining rewards that form part of Ethereum (ETH) transaction fees. Therefore, Ethereum gas is valued in Ethereum (ETH). Gas costs are commonly referred to as gas bills or gas costs.
Ethereum gas fees are effectively quoted in ETH, but the actual amount may be less compared to the value of ETH. Therefore, gas costs are usually expressed in gwei, which is one billionth of ETH, or 0.000000001 ETH.
Ethereum runs on the basis of smart contracts processed by the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). Virtual machines require a dedicated programming language. The language of EVM is Solidity.
Each line of code in Solidity uses a certain amount of gas to run. The ERC-20 token is one of the simplest form of smart contract running on Ethereum and contains only 9 rules. This means that multiple lines of solidity are not required to write an ERC-20 token contract.
However, more sophisticated smart contracts, such as MakerDAO’s Collateralized Debt Position contract, which issues the DAI (Dai) stablecoin, include more lines of solidity code. That is why it inevitably costs more to execute a complex smart contract than a simple ERC-20 token transfer.
The term ‘gas’ is appropriate because it fits the car analogy well. Think of ‘gas’ like the oil you put in your car and the execution of Ethereum transactions is like driving a car. You get gas from the miners just like you add oil at a gas station. Continuing this analogy, just like paying gas station staff for gas, Ethereum gas bills are paid to miners in ETH.
How to set gas cost?
There is no fixed gas fee in ETH or USD. The gas fee is effectively set based on a fee agreed upon by Ethereum users and miners. It is important to remember that Ethereum, like most blockchains, operates on the principle of incentives. Miners take part of the transaction fee as a profit.
Therefore, the gas fee paid for the transaction must include computing power and be attractive enough to process the transaction.
Ethereum miners can also choose which transactions to include in the block they want to mine next. In this way, miners choose the transaction that offers the most profit potential, so you can think of Ethereum users as bidding for a space in the next block to be mined by miners.
Gasbee’s economic model explains why the price rises when traffic on the Ethereum network increases. As more people line up to process transactions, miners can be more picky about which transactions to include in their blocks. This means that the user has to bid a higher gas price so that their trade does not lag behind other more profitable trades.
Invets in Ether with a low cost on Bybit
Ethereum gas limit – Ethereum Gas Station
The standard gas limit for most basic Ethereum transactions is 21,000 gas. You can use a site like EthGasStation to calculate your transaction costs. If you look at the capture below, the current average gas cost is 123 gwei, and the standard gas limit is arbitrarily set at 21,000 gas.
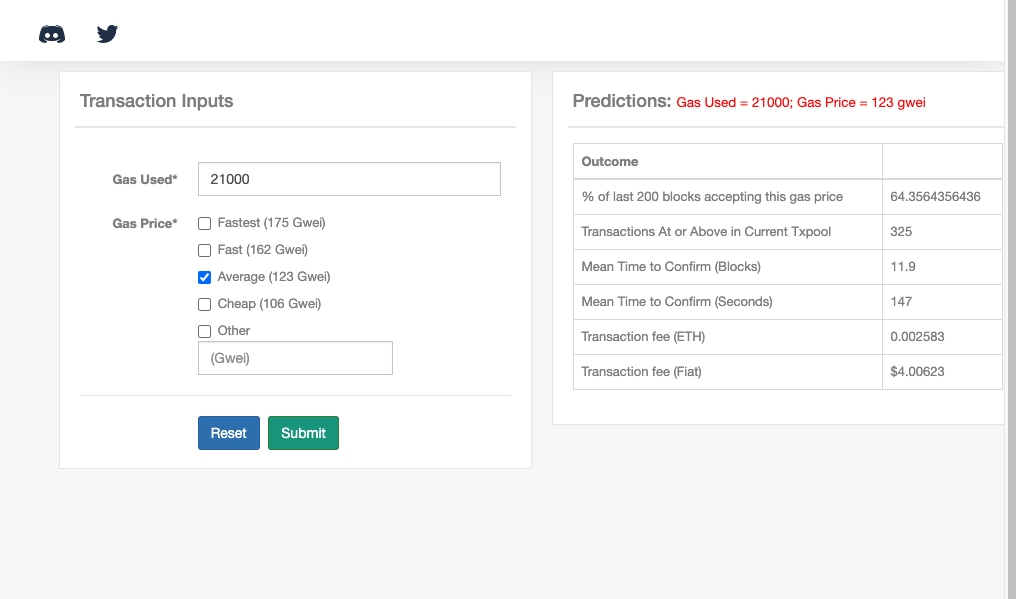
In that image, you can see some important indicators that tell you the value of the transaction and the speed of confirmation. For example, about two-thirds of miners, about 64%, will process a transaction at that price, and accepting a fee of 0.002 ETH or $4 will take 147 seconds or 11.9 blocks to confirm the transaction.
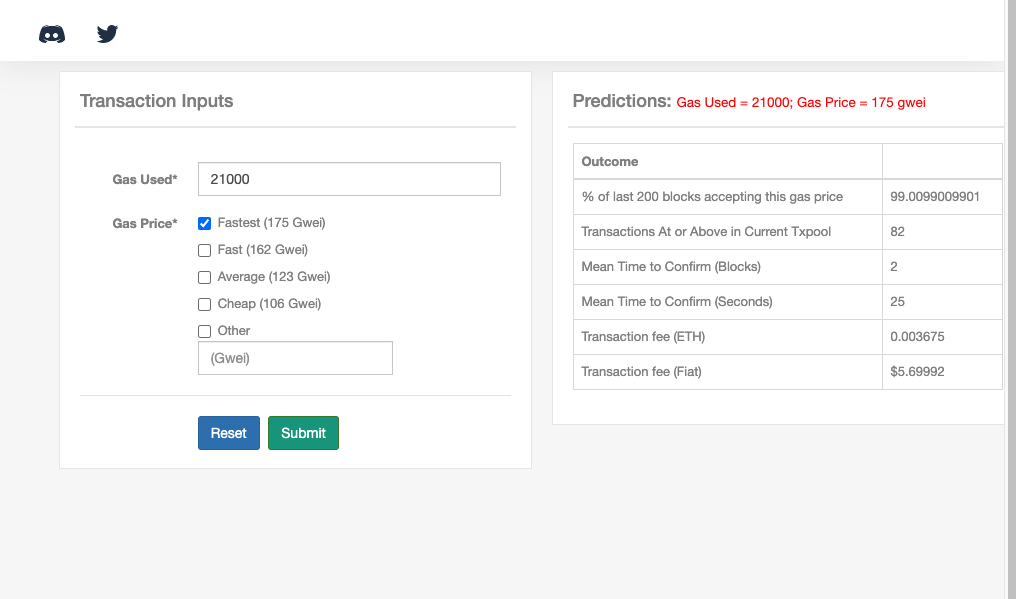
If you want to get verified faster, even if it costs more, you can cut the verification time down to 25 seconds, but you will have to pay a transaction fee of around $5.70 based on the gas limit of 21,000 gas.
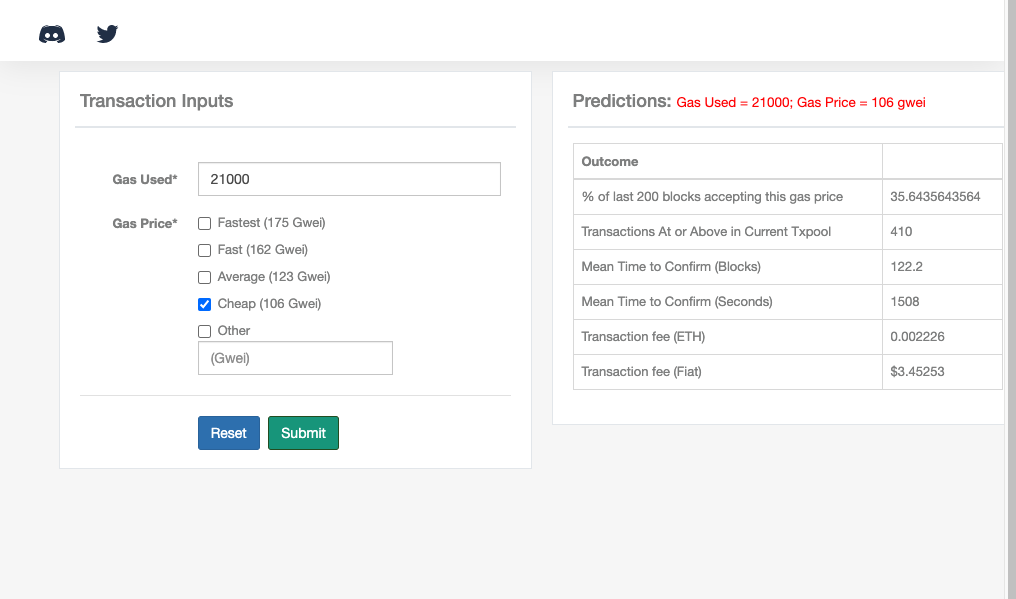
If you can afford to wait a little longer, you can also trade 21,000 gas for $3.45.
What if you lower your gas limit?
At this point, you may be asking if it’s okay to reduce the amount of gas you use to trade. So you may be wondering what would happen if you didn’t use all of your 21,000 gas. You can, of course, set a lower gas limit, but in principle, the remaining gas will be refunded, so it might be a good idea to give it a little leeway.
There is a balance between high and low-cost and gas. We’ve already looked at the cost side. The higher gas cost provides more incentives for miners.
But gas is the computing power needed to get the job done. Lowering the gas limit carries a risk as you may not have enough gas to count your trades.
When the gas is exhausted, the miner will stop processing as is and return the smart contract to its previous state. The attempted transaction is recorded on the Ethereum blockchain and the miner still has to pay the fee because the contract has been terminated.
Conversely, excessively increasing the gas limit can make the trade less likely to be picked up. Each Ethereum block is capped at 6.7 million gas. Even if part of the gas limit is returned to the initiator, the gas limit of the transaction is still counted as part of the block. Therefore, if you choose a transaction with an incorrect gas limit, there is no benefit because the number of transactions that can be placed in a block is reduced accordingly.
In many ways, Ethereum’s gas scheme is a well-designed scheme based on the principles of a market economy. But it’s not a perfect scheme, as you can see from the crowded times when users struggle with astronomical rates. Running a game-like app that uses microtransactions on the Ethereum blockchain is truly prohibitively expensive.
In addition, since gas fees must be paid in ETH, an ETH balance is always required, even if the underlying token of the application is different. This can be a hassle for users and developers.
As Ethereum transitions to proof-of-stake and sharding with its Ethereum 2.0 upgrade, a solution to these issues may emerge. With the growing penetration of Layer 2 platforms, it may gradually become unnecessary to develop directly on Ethereum. However, given the ecosystem already established on Ethereum, the platform itself is likely to remain an important part of the blockchain environment for the time being.
Please check Bybit official website or contact the customer support with regard to the latest information and more accurate details.
Bybit official website is here.
Please click "Introduction of Bybit", if you want to know the details and the company information of Bybit.



Comment by Hans
April 24, 2024
as I am trading here various assets, for me it's the most important feature. i mean, flexibility in tradable markets. i alternate trading styles, meaning that sometimes I trad...