What are Public and Private Keys in Cryptocurrency markets? What are the differences?
Public vs Private Keys. Table of Contents
- Public vs Private Keys
- What are a public key and a private key?
- Cryptocurrency used in cryptocurrencies
- How private and public keys work
- Difference Between Public Keys and Private Keys
- Advantages and Limitations of Public Key and Private Key Encryption
- When should you choose public-key or private-key encryption?
- Conclusion

Public vs Private Keys
Cryptocurrency is the heart of cryptocurrency.
Without encryption, no transaction would be secure, and the integrity of the information would not be maintained. When performing peer-to-peer (P2P), i.e., person-to-person transfers, data can be exposed without secure encryption and attempts to read data structures without knowing that the data has been tampered with.
At this point, private keys and public keys play a very important role in authorizing transactions.
Although public and private keys both strive to secure transactions, they are distinctly different in purpose.
To compare them, the public key is used to verify the transaction after the transaction is requested.
And in general, a public key is also understood as an ‘address’ to receive cryptocurrency.
On the other hand, the private key associated with a cryptocurrency account focuses on transaction authorization.
In general, the private key is not shared and should only be known by the owner.
In other words, if someone has been granted access to your private key, your wallet may lose its assets.
This is why you need to understand what private and public keys are and why they are so important.
Perhaps you can also learn how to avoid becoming a person who takes millions of dollars out of Bitcoin.
What are Public & Private Keys and Public Address?
What are a public key and a private key?
A public key and a private key are basically used to decrypt a message encrypted with a complex mathematical algorithm within the encryption method.
The public key can be widely distributed, but the private key used in an encrypted sense is kept separately as a password to protect digital assets.
These private keys usually use 256-bit encryption, but it depends on the type of cryptocurrency.
This includes BTC, ETH, LTC, and more. For example, a Bitcoin private key is formed with the following values:
0x01 and 0xFFFF FFFF FFFF FFFF FFFF FFFF FFFF FFFE BAAE DCE6 AF48 A03B BFD2 5E8C D036 4140, representing nearly the entire range of 2256-1 values.
An example public key is:
3048 0241 00C9 18FA CF8D EB2D EFD5 FD37 89B9 E069 EA97 FC20 5E35 F577 EE31 C4FB C6E4 4811 7D86 BC8F BAFA 362F 922B F01B 2F40 C744 2654 C0DD 2881 D673 CA2B 4003 C301 0001 E2 CD CB02 0
A key is a symbolic sequence that can be used by all users (public key) or known only to the owner (private key), and is randomly formed. The public key is used for encryption, but information can also be decrypted using only the private key.
If you know the private key, you can get the public key, but it’s almost impossible to find the private key with the public key.
Cryptocurrency wallets are great examples of public and private key uses.
In a wallet, the public key is the user’s address, which tells where the wallet is from which can send tokens to other network participants.
However, in order for users to transfer passwords between each other, they need their private keys to confirm the transaction.
This means you will need a password, just like logging into your email.
An e-mail address is a fixed point from which other e-mail network participants can send mail. A password is required to gain full access to your email account.
But for the longest time, symmetric encryption has been the default type of encryption where all messages are encrypted and decrypted with the same code (key).
Still, it was difficult to fully trust the security capabilities of symmetric encryption.
Therefore, symmetric encryption is designed to solve this security problem with a pair of keys (one public and one private) that are used separately to encrypt and decrypt messages.
Unlike symmetric encryption, which uses a single key to encrypt and decrypt information, the public and private keys must “match” the encrypted data.
They are created and used at the same time.
So how are they used for encryption?
What are Cryptography and Digital Signature?
Cryptocurrency used in cryptocurrencies

When it comes to encryption of cryptocurrencies, there are several methods such as symmetric encryption, asymmetric encryption, and hashing.
Hashing
Hashing is designed to cryptographically replace a user’s account address in order to encrypt transactions between accounts.
Random letters and numbers are appended to the stored value to keep the password secure.
This is primarily to mitigate the risk of cracking passwords by making them harder.
Stored values refer to digital fingerprints or hashes when conversion is complete.
Symmetric Encryption
It is the most widely used and one of the easiest and most effective encryption.
Messages are encrypted with a single key, which may or may not be the same.
It is then sent to the recipient and decrypted upon receipt and confirmation.
Asymmetric Encryption
Unlike symmetric encryption, in asymmetric encryption, encryption and decryption of a message usually involves two keys: a private key and a public key.
The public key is used to verify the transaction after the transaction is requested.
A private key, on the other hand, decrypts a message or transaction.
The concept is to maintain the authenticity of the transaction and prevent the security from being compromised.
That is, if you lose your private key, there is no way to retrieve it.
Similarly, if the private key is exposed, all transactions can be allowed, and since it has been publicly recognized, it cannot be recovered.
How private and public keys work
There are two main use cases for public keys encryption: identity and confidentiality.
It can be simply described in the following way:
- The sender gets the recipient’s public key.
- The sender uses this key to encrypt the information.
- The sender sends encrypted information to the recipient.
- The recipient uses the private key to decrypt the data.
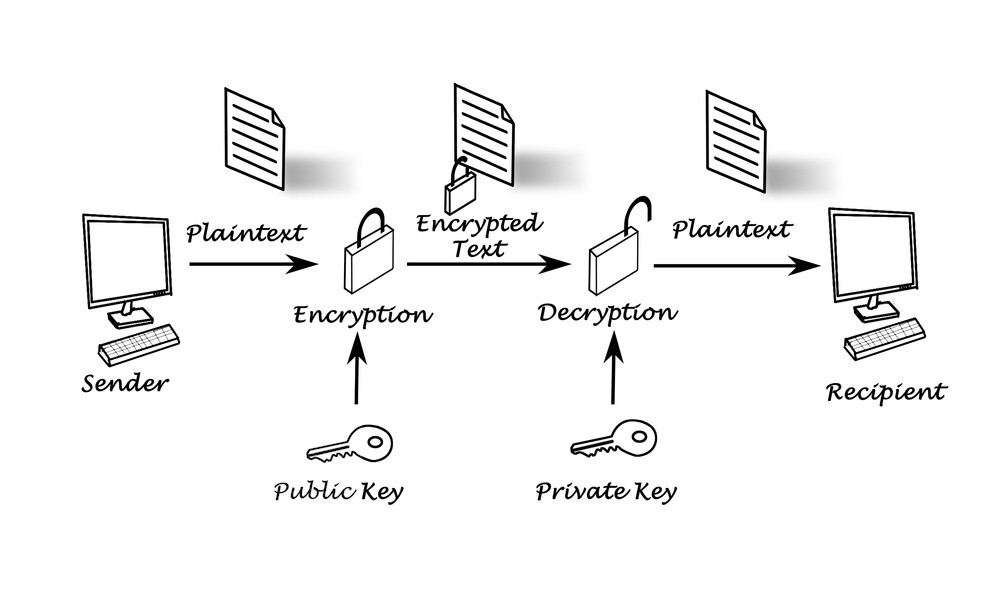
Suppose Alex (sender) wants to send 1 BTC to Jane (recipient).
Alex knows Jane’s public key and uses it to encrypt the transaction.
Jane receives the transaction and decrypts Alex sending 1 BTC with her private key.
Because no one knows her private key, only Jane can authorize the transaction.
When it comes to cryptocurrencies, your private key is something you physically own.
The private key proves that you have authority to manage your digital assets and authorize all transactions.
Anyone who knows this key will be able to use the associated funds.
Cryptocurrency Trading – Best Strategies, Worst Mistakes and Myths
Difference Between Public Keys and Private Keys
Both private and public keys are aimed at verifying that a particular transaction has been used by the signing party and has not been falsified.
Although their purpose is similar, private and public keys are different in many ways.
Here’s what you need to know:
Algorithms and Mechanisms
Public key cryptography requires two separate keys for encryption and decryption.
The private key is for the owner only and the public key can be used by anyone.
One key is required for transmission between two parties involved in symmetric key encryption.
The same private key is used to encrypt and decrypt information.
The private key is shared between the sender and the recipient of an encrypted message.
Performance
Private key mechanisms are much faster than public keys. This is because a private key requires only one key, whereas a public key requires two keys.
Privacy
The private key is confidential and is not disclosed to anyone other than the wallet owner.
If the private key is lost, it cannot be restored and encrypted files become unusable.
As a rule, these keys contain complex numbers and are difficult to remember.
The security of a private key depends entirely on what the owner does. The best way to keep your private key safe is to use offline storage.
On the other hand, the public key is open to all users.
You won’t lose your ‘public’ key.
Digital signature
Web content can be digitally signed with the user’s private key and verified with the user’s public key.
This makes it easier for the network to identify the sender of the message while ensuring that a trusted identity sent the message.
Digital signatures provide the following security benefits:
- Authentication:
- Since it cannot be forged, it can prove that a message or user is legitimate or not.
- Non-rejectable:
- After communication, the sender of the message cannot reject the signature.
- Authenticity:
- The signature serves as a guarantee that the received message has not been altered.
Start investing in Crypto markets today
Encryption and decryption
The contents are encrypted with the user’s public key and can only be decrypted with the private key.
This is the only way to change the message direction.
Encryption provides the following security benefits:
- Privacy:
- No unauthorized access. Confidentiality is maintained by using a private key that is unknown to anyone but the owner.
- Integrity:
- An encryption process with a secure public key ensures that messages received are not tampered with.
Public key cryptography is used in numerous protocols and data formats implemented by various applications and system software.
These include SSL protocols, SSH, digitally signed PDF files, OpenPGP, S/MIME, and more.
It is widely applied to software programs such as browsers to ensure a secure connection on unstable networks.
Asymmetric cryptography forms the basis of blockchain algorithms, which form the basis of all cryptocurrencies.
Advantages and Limitations of Public Key and Private Key Encryption
There is no perfect methodology or encryption. This includes public and private keys.
The pros and cons of public and private keys are as follows.
Advantages
Private key encryption technology is a great way for any business to protect sensitive information.
Whether you choose symmetric or asymmetric encryption, both have their advantages and disadvantages, just like any other technology.
Symmetric encryption is faster and easier to perform.
The system uses a reversible formula to encrypt or decrypt a file. Therefore, this method requires less computer resources than asymmetric encryption.
At the same time, private key encryption provides a much higher level of security, but there are still some problems here.
The main problem with this method is key transfer.
Sending the key requires an insecure form of communication.
Giving third parties access to the key to unlock your data is risky.
This method cannot guarantee the origin and authenticity of the message, and any disputes or doubts may cause problems.
Users must create and manage multiple private keys to segregate data or funds between groups.
Too many keys can be inconvenient, and a newly shared key with all other participants can weaken security.
Disadvantages
The disadvantages of using private and public keys are related to some serious weaknesses they have.
First, losing your private key will have dismal consequences.
In other words, the loss of the private key means that no one can decrypt the received data.
In terms of cryptocurrency, wallet owners lose access to their wallets if their private keys are lost.
Start investing in Cryptocurrencies
When should you choose public-key or private-key encryption?
You can choose the encryption method according to your preference and convenience.
Symmetric encryption is useful when speed and data protection are a concern.
For example, symmetric encryption algorithms with Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) adopted are used by companies such as Apple and Microsoft.
Also, if your focus is on storing your data, symmetric encryption is ideal.
Works well even when encrypted data is stored on the device and that data is not being transmitted
Asymmetric encryption is a good choice if security enhancements are a priority over speed and computing power.
Since authentication is not supported with symmetric encryption, asymmetric encryption should be used when identity verification is required.
Blockchain technology relies on identity verification to authorize transactions.
Therefore, cryptocurrency traders and investors will prefer to use asymmetric crypto.
Conclusion
As the world shifts into a digital realm, data storage and security becomes increasingly important.
In public-key cryptography, it helps users to be reasonably secure because no one knows the private key paired with the open public key.
It plays a beneficial role in avoiding potential interception and cyber fraud.
The most important thing here is to keep your private key safe and ensure that no one else has access to your private key.
Starting a trade is difficult, but securing your funds is even more difficult.
We strongly encourage you to protect your data and encourages you to learn about privacy, data protection, and trust.



Comment by Hans
April 24, 2024
as I am trading here various assets, for me it's the most important feature. i mean, flexibility in tradable markets. i alternate trading styles, meaning that sometimes I trad...