How does a transaction of Bitcoin work?
How does a Bitcoin transaction work?
A Bitcoin transaction is signed information for the purpose of transferring ownership of a specified amount of Bitcoin from one individual to another. A transaction records all information including the sender’s unused bitcoins, the remittance information (represented by the transaction ID or transaction hash), the amount of the remittance, and the recipient’s public address. Transactions are broadcast to the Bitcoin network for validation, and once they pass validation, they go to an online ledger called the blockchain for remittance. Verified transactions are added to information blocks, and those blocks are linked to other blocks to create a blockchain.
To make it easier for you to understand the principles of blockchain transactions, we have put together pictures and detailed explanations below. In the example, we use the person’s name for ease of explanation, but one of the key advantages of Bitcoin transactions is anonymity, so the counterparties cannot share each other’s personal information. In fact, all that is needed to complete a Bitcoin transaction is the addresses of the sender and recipient.
What is Bitcoin? How people are using this currency?
Bitcoin transaction input and output values
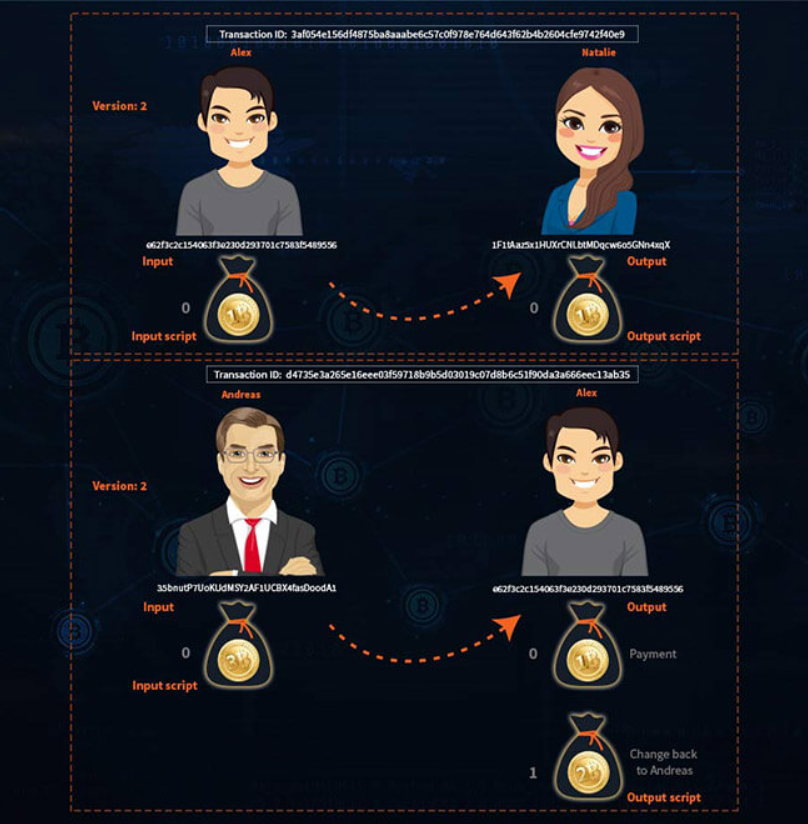
When Alex sends 1 Bitcoin to Natalie as a payment, the transaction will look like this:
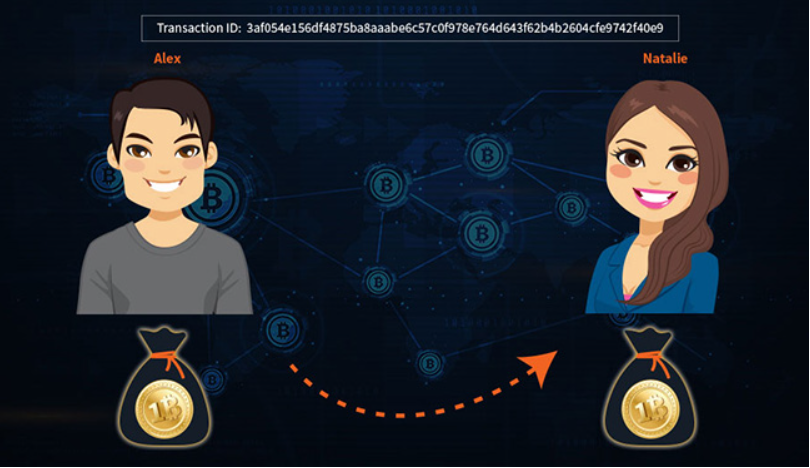
This is a simple form of a Bitcoin transaction, but adding other information makes it a bit more complex. For example, Alex’s 1 Bitcoin is the payment received from Andreas in the previous transaction. What Alex receives from Andreas is the input value of the transaction, and what Alex sends as payment to Natalie is called the output value. The input always shows the source and the amount of bitcoins, the output shows the destination and the amount of bitcoins Natalie will receive.
Knowing this, a Bitcoin transaction can be described as:
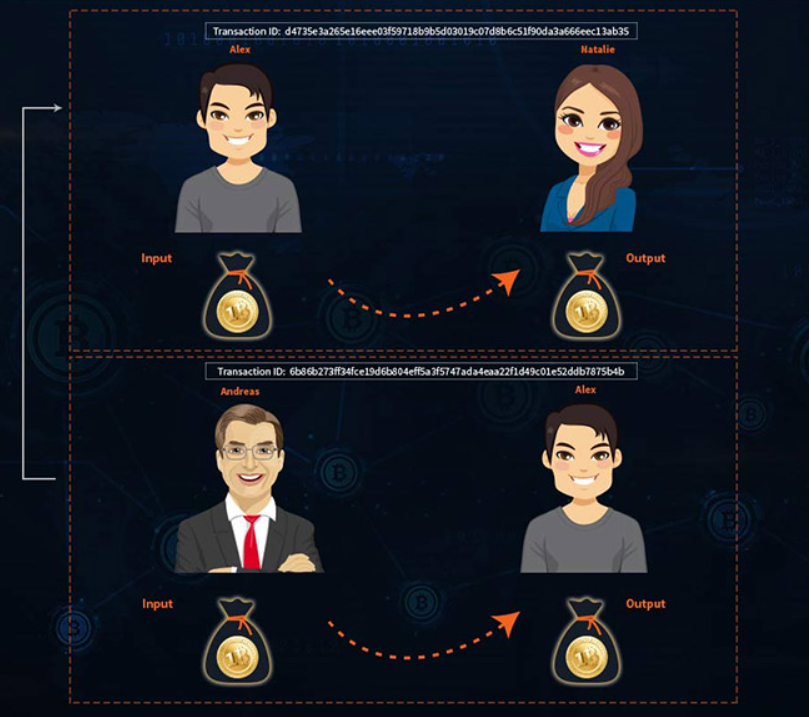
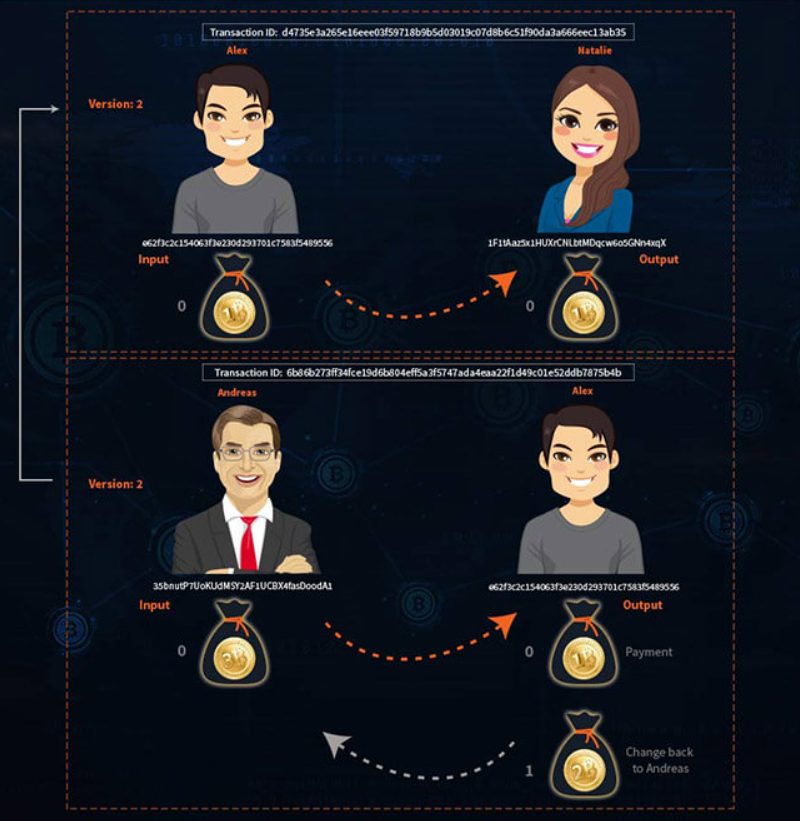
Although in the example there is only one input and one output, a Bitcoin transaction can contain multiple inputs and outputs. A Bitcoin transaction contains a list of inputs and outputs, each with its own index and sequence number. Number 0 is always considered the first item.
Notice the change in the input and output values of the first transaction between Andreas and Alex. Andreas has 3 bitcoins sent from a customer in a previous transaction and needs to send 1 bitcoin to Alex. The amazing thing about the Bitcoin protocol is that cryptocurrencies are indivisible. In other words, it is impossible for Andreas to send only 1 Bitcoin to Alex in this case. Instead, Andreas sends Alex all 3 Bitcoins and receives 2 Bitcoins in balance.
List of Cryptocurrency exchanges
Bitcoin Transaction security
After receiving the bitcoins from Andreas, Alex must prove that he is the party so he can send bitcoins to Natalie. To do this, Alex has to “unpack” the input script with his private key. For more information about private keys, see Bitcoin Keys and Addresses.
Once Alex has unlocked the script, he can proceed and spend the bitcoins in the input. In order for Natalie to be able to spend the money she received from Alex, the cycle continues as Alex needs to create a script that Natalie needs to solve. Additional information is included in the transaction history, such as transaction version, lock time (the time the transaction is added to the blockchain), and other detailed rules to be followed.
Finally, as with all financial transactions, there is some sort of identification. In the case of Bitcoin, it is verified in the form of a transaction ID.
When a transaction is created, it is forwarded to another node for the validation process. The Bitcoin network node then examines the information in that transaction for verification purposes. Are all the information available? Are the unused bitcoin amounts real and unused? No double-spending problems? Is the transaction signature valid?
Once validated, the transaction is confirmed and added to the transaction block for the next step. This is the mining part, which we will cover in the future as it is necessary for a transaction to be within the blockchain.