Sign up on Binance and open an Options trading account.
What is Options Contract?
An options contract is an agreement that allows traders to buy or sell an asset at a predetermined price before or on a specific date. While options contracts may sound similar to futures contracts, traders who buy options contracts are not obligated to settle their positions.
Options contracts may be derived from a variety of underlying assets, including stocks and cryptocurrencies. These contracts may also be derived from financial indices. Options contracts are often used to hedge existing positions and to engage in speculative trades.
Open Binance’s Options account
How do options contracts work?
Options are divided into two basic types, call options and put options. A call option gives the contract owner the right to buy the underlying asset, while a put option gives the contract owner the right to sell the underlying asset. As a result, traders typically choose a call option when the underlying asset price is expected to rise and a put option when the price is expected to fall. They may also use calls and puts, or even a combination of the two, to bet on market volatility with the aim of keeping prices stable.
An option contract consists of at least four parts: size, expiration date, strike price and premium. First, order size refers to the number of contracts to be traded. Second, the expiration date is the date when the trader can no longer exercise the option. Again, the strike price refers to the price at which the asset is bought and sold (if the contract buyer decides to exercise the option). Finally, the premium refers to the price at which the options contract is traded. This price represents the amount an investor must pay to obtain an option. Thus, the buyer gets the contract from the writer (seller) based on the value of the premium, which is constantly changing as the expiration date approaches.
Basically, if the strike price is lower than the market price, traders will buy the underlying asset at a discount, and after taking the premium into account, they may choose to exercise the contract and profit from it. However, if the exercise price is higher than the market price, there is no reason for the holder to exercise the option, and the contract will be deemed invalid. If the contract is not exercised, the buyer only loses the premium paid when the position was opened.
It is important to note that while the buyer can choose whether to exercise the call and put options, the action of the writer (seller) depends on the buyer’s decision. That is, if the buyer of a call option decides to exercise its contract, the seller is obliged to sell the underlying asset. Likewise, if a trader buys a put option and decides to exercise it, the seller is obligated to buy the underlying asset from the contract holder. This means that writers face a higher risk than buyers. While the buyer’s loss is limited to the premium paid for the contract, the writer’s loss may be greater depending on the market price of the asset.
Some contracts give the trader the right to exercise the option at any time before the expiration date. Such contracts are often referred to as American options contracts. In contrast, European-style options contracts are only exercised on the expiry date. But it’s worth noting that the names of these contracts have nothing to do with their geographic locations.
Go to Binance’s Official Website
Option premium
The value of the premium is affected by a number of factors. In simple terms, we can set the premium for an option to depend on at least four factors: the price of the underlying asset, the strike price, the time remaining until expiration, and the volatility of the corresponding market (or index). These four components have different effects on the premium of call and put options, as shown in the table below.
| Call option premium | Put option premium | |
|---|---|---|
| Asset prices rise | Rise | Decline |
| Exercise price increases | Decline | Rise |
| Time reduction | Decline | Decline |
| fluctuation | Rise | Rise |
We can easily see that asset prices and strike prices have opposite effects on call and put premiums. In contrast, shorter times generally mean lower premiums for both options. The main reason is that the shorter the time period, the less likely the traders are to turn the contract in their favor. On the other hand, rising volatility levels usually lead to higher premiums. Therefore, option contract premiums are the result of a combination of these and other factors.
Open Binance’s Options account
Option price sensitivity
Option price sensitivity is a tool used to measure some of the many factors that affect the price of a contract. Specifically, they are statistical values that measure the risk of a particular contract against different underlying variables. Below is a brief description of some key option price sensitivities and what they measure:
- Delta:
- A measure of how much the option contract price changes relative to the price of the underlying asset. For example, a Delta of 0.6 means that for every $1 change in the asset price, the premium may change by $0.60.
- Gamma:
- Measures the rate of change of Delta over time. Assuming the Delta changes from 0.6 to 0.45, the option’s Gamma is 0.15.
- Theta:
- Measures the price change associated with a contract time shortening by one day. It shows how the premium is expected to change as the expiration date of the options contract approaches.
- Vega:
- Measure the corresponding change rate of the contract price for every 1% change in the implied volatility of the underlying asset. An increase in Vega usually reflects an increase in the price of calls and puts.
- Rho:
- A measure of expected price changes related to interest rate fluctuations. Rising interest rates generally lead to higher call options and lower put options. Therefore, a call option has a positive Rho value and a put option has a negative Rho value.
Common Use Cases
1. Hedge Strategy
Options contracts are widely used as hedging tools. A very basic example of a hedging strategy is where a trader would buy a put option on an already held stock. If the overall value of a major holding is lost due to a drop in price, exercising a put option can help a trader mitigate losses.
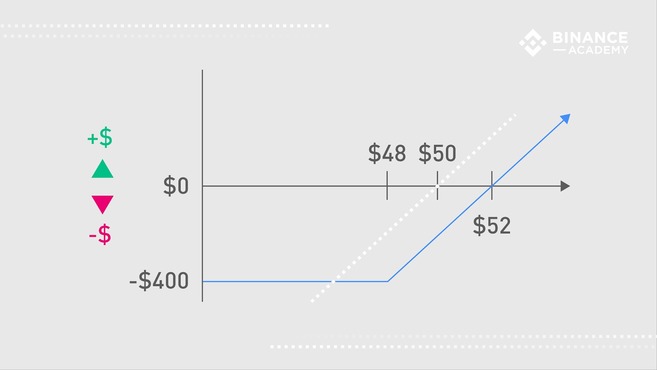
For example, suppose Alice buys 100 shares of stock at $50 in the hope that the market price will rise. But to hedge against the possibility of a drop in the share price, she decides to buy a put option with a strike price of $48 and pay a premium of $2 per share. If the market turns bearish and the stock falls to $35, Alice can exercise the contract to mitigate her losses and sell her stock at $48 per share instead of $35 per share. But if the market turns bullish, then she doesn’t need to exercise the contract and only loses the premium paid ($2 per share).
Thus, Alice would break even at $52 ($50 per share + $2) and her loss would be capped at $400 ($200 sell the stock at a maximum loss of $200).
2. Speculative trading
Options are also widely used in speculative trading. For example, a trader who believes an asset price is about to rise might buy call options. If the asset price is higher than the strike price, the trader can exercise the option and buy at a discount. When the price of the asset is above or below the strike price, making the contract profitable, the option is called an “in-the-money option.” Correspondingly, if the contract is at the break-even point, it is called an “at-the-money option”, and if it is at a loss, it is called an “out-of-the-money option”.
Go to Binance’s Official Website
Basic strategy
When trading options, traders can employ a variety of strategies based on four basic positions. The buyer can buy a call option (right to buy) or a put option (right to sell). Writers can sell call or put contracts. As mentioned earlier, if the contract holder decides to exercise the option, the writer is obliged to buy or sell the asset.
There are different options trading strategies to choose from based on the various possible combinations of call and put contracts. Some basic examples of these strategies are: Protected Puts, Covered Calls, Straddles, and Straddles.
- Protective Put Option:
- A put option contract that involves buying an existing asset. This is the hedging strategy Alice used in the previous example. This strategy is also known as portfolio insurance because it protects investors from potential downtrends while maintaining their exposure in case asset prices rise.
- Covered Call:
- A call option that involves the sale of an existing asset. Investors can earn additional income (option premiums) from their stock holdings through this strategy. If the contract is not exercised, the investor can earn a premium while retaining the asset. But if the contract is exercised due to a rise in the market price, the investor is obliged to sell the position.
- Straddle:
- Refers to buying a call option and a put option on the same asset at the same strike price and expiration date. As long as the price of an asset rises or falls by a large enough amount, traders are able to profit. Simply put, traders are betting on market volatility.
- Strangle:
- Involves buying “out of the money” calls and puts at the same time (that is, buying a call with a strike price above the market price and buying a put option with a strike price below the market price). Wide straddle arbitrage is basically the same as straddle arbitrage, but the cost of opening a position is lower. However, straddle arbitrage requires higher volatility levels to be profitable.
Open Binance’s Options account
Advantages
- Suitable for hedging market risk.
- More flexibility in speculative trading.
- Various combinations and trading strategies with unique risk/reward patterns are available.
- It is possible to profit from all market trends (bulls, bears and bulls).
- It can reduce the cost of opening a warehouse.
- Multiple transactions are allowed at the same time.
Disadvantages
- The mechanics of operation and the calculation of premiums are sometimes not easy to understand.
- High risk involved, especially for writers (sellers).
- Trading strategies are more complex than traditional alternative strategies..
- The options market is often plagued by low levels of liquidity, making it less attractive for most traders.
- The premium value of an options contract fluctuates widely and decreases as the expiration date approaches.
Go to Binance’s Official Website
Options and Futures
Both options contracts and futures contracts are derivatives and therefore present some of the same use cases. Despite the similarities, there are huge differences in the settlement mechanism.
Unlike options, futures contracts are usually exercised on the expiration date, which means the contract holder is legally obligated to trade the underlying asset (or cash with their respective value). On the other hand, options can only be exercised at the discretion of the trader holding the contract. If the contract holder (buyer) exercises the option, the writer (seller) is obliged to trade the underlying asset.
Summary
As the name suggests, options allow investors to choose to buy or sell an asset in the future, regardless of market price. Such contracts are versatile and can be used in a variety of situations: not only for speculative trading, but also for executing hedging strategies.
But it’s worth noting that trading options and other derivatives involves many risks. Therefore, before using this type of contract, traders should carefully understand how it works. It is also important for traders to fully understand the different combinations of call and put options and the potential risks involved with each strategy. In addition, traders should also consider adopting risk management strategies as well as technical and fundamental analysis to control potential losses.
Open Binance’s Options account
Please check Binance official website or contact the customer support with regard to the latest information and more accurate details.
Binance official website is here.
Please click "Introduction of Binance", if you want to know the details and the company information of Binance.



