What is cryptocurrency mining?
Cryptocurrency mining is the process of validating transactions on the blockchain and creating new coins of cryptocurrency. Miners require a lot of computing resources, which also ensures the security of the blockchain network. Honest and successful miners are able to earn newly created cryptocurrency and transaction fee rewards.
Introduction
Mining is the process of validating cryptocurrency transactions between users and adding them to the blockchain public ledger. Mining operations are also responsible for introducing new coins into the existing circulating supply.
Mining is a key factor that allows the Bitcoin blockchain to be used as a distributed ledger. All transactions are recorded in a peer-to-peer network without the need for a central authority to intervene. This article will discuss the mining process in the Bitcoin network, but the mining process is similar for altcoins that use the same mining mechanism.
How mining works
After a new blockchain transaction is concluded, it will be sent to the mining pool, which we call the mempool. The job of the miners is to verify the validity of these pending transactions and integrate them into blocks. You can think of blocks as pages of a blockchain ledger, where transactions (and other data) are recorded.
Specifically, mining nodes are responsible for collecting unconfirmed transactions from the mempool and integrating them into candidate blocks. Subsequently, miners attempt to convert this candidate block into a validly confirmed block. But they need to be able to solve complex math problems. This requires a lot of computing resources, but miners are issued a block reward for each successfully mined block, including the newly created cryptocurrency and transaction fees. Let’s take a closer look at the mining process.
Go to Binance’s Official Website
Step 1 – Hash the transaction
To mine a block, the first step is to operate the pending transactions one by one from the mempool through the hash function and submit them. Every time we submit a piece of data through a hash function, we generate a fixed-length output called a hash. During the mining process, the hash of each transaction consists of a string of numbers and letters used as an identifier. The transaction hash value represents all the information contained in that transaction.
In addition to hashing and singling out each transaction, miners add custom transactions that send block rewards to themselves. This transaction, called a Coinbase transaction, enables the creation of new coins. In most cases, Coinbase transactions are the first to be recorded in a new block, followed by pending transactions that they want to verify.
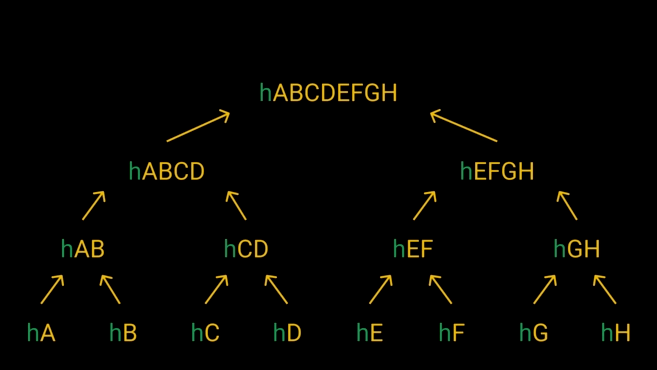
Step 2 – Create Merkle Tree
After each transaction is hashed, the hashes are combined into a structure called a Merkle tree. Merkle tree, also known as hash tree, works by combining transaction hashes into pairs and then hashing them. The new hash outputs are combined into pairs, hashed again, and the whole process is repeated until a single hash is created. The last hash also called the root hash (or Merkle root), basically represents all previous hashes used to generate the root hash.
Step 3 – Find a valid block header (block hash)
The block header is used as the identifier of each independent block, representing that each block has its own hash value. When creating a new block, miners combine the hash of the previous block with the root hash of the candidate block to generate a new block hash. In addition to these two elements, they also need to add a random value called nonce.
Therefore, when miners try to validate their candidate block, they need to combine the root hash, previous block hash and nonce and submit it through the hash function. Its goal is to create a hash that is considered valid.
The root hash and the hash of the previous block cannot be changed, so miners need to make multiple changes to the nonce until a valid hash is found.
The output (block hash) must be less than some target value determined by the protocol to be considered valid. In Bitcoin mining, the first few digits of the block hash must be zeros. This is what we call mining difficulty.
Step 4 – Propagating mined blocks
As we can see, miners need to repeatedly hash the block header with different nonce values. They keep repeating this work until they find a valid block hash. The miner found will propagate his block to the network. All other nodes will check that the block and its hash are valid, and if so, add the new block to the copy of the blockchain.
At this point, the candidate block becomes a confirmed block and all miners move on to the next block. Miners who cannot find a valid hash in time will discard their candidate blocks and continue mining.
Mining difficulty adjustment
The mining difficulty is regularly adjusted by the protocol, ensuring that the rate at which new blocks are created remains the same. This is why new coin issuance is stable and predictable. The difficulty adjustment is proportional to the computing power ( hash rate ) invested in the network.
Therefore, every time a new miner joins the network, competition intensifies, hashing difficulty increases, and the average block time cannot be reduced. Conversely, if many miners decide to leave the network, the hashing difficulty will decrease, and the difficulty of mining new blocks will decrease. This adjustment allows the block time to remain constant regardless of the network hashing power.
Go to Binance’s Official Website
What if two blocks are mined at the same time?
Sometimes two miners broadcast a valid block at the same time, and the network ends up with two competing blocks. Miners will start mining the next block based on the block received first. This caused the network to temporarily split into two different versions of the blockchain.
The competition between these blocks will continue until miners mine a new block based on any block. The first block to mine a new block will be considered the winner. Abandoned blocks are called orphan or stale blocks, and all miners who choose this block will move to the same chain as the winning block to continue mining.
Are all cryptocurrencies mineable?
Bitcoin is the most popular and well-established of all the cryptocurrencies available for mining, but not all cryptocurrencies are mineable. Bitcoin mining is based on a consensus algorithm called Proof of Work (PoW).
Proof of Work (PoW)
Proof of Work (PoW) is a traditional block consensus mechanism created by Satoshi Nakamoto. The concept first appeared in the Bitcoin white paper published in 2008. Simply put, Proof of Work determines how a blockchain network can reach consensus among all distributed participants without a third-party intermediary. It requires a lot of computing power to reach consensus and, by doing so, deter malicious behavior.
As we have seen, in a proof-of-work network, transactions are verified by miners. To gain the right to mine the next block, miners compete by solving complex cryptographic puzzles using specialized mining hardware. The first miner to successfully find an efficient solution can propagate their block of transactions to the blockchain, earning block rewards.
The number of cryptocurrencies for block rewards varies across blockchains. For example, as of December 2021, miners can earn 6.25 BTC block rewards from the Bitcoin blockchain. According to the halving mechanism, the number of bitcoins in the block reward is halved every 210,000 blocks (about every 4 years).
Go to Binance’s Official Website
Different cryptocurrency mining methods
There is not only one way to mine cryptocurrencies. As new hardware and consensus algorithms continue to emerge, equipment and processes are being optimized. Miners typically use specialized computing devices to solve complex encryption equations. Let’s take the most common mining methods as an example.
1. Central Processing Unit (CPU) Mining
Central processing unit (CPU) mining refers to the use of a computer’s CPU to perform the hash functions required for proof-of-work. In the early stages of Bitcoin, mining costs and barriers were low. Mining puzzles can be handled by ordinary CPUs, so anyone can try to mine Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies.
However, as more and more people started mining, and the hash rate of the network increased, it became more and more difficult to mine profitably. In addition, with the rise of professional mining hardware with higher computing power, CPU mining is almost a thing of the past. Today CPU mining is no longer feasible because miners use specialized hardware.
2. Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) Mining
Graphics processors are designed for parallel processing of a range of applications. It is commonly used in video games or rendering graphics, and it can also be used for mining.
GPUs are relatively inexpensive and more flexible than popular application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC) mining hardware. Some altcoins can be mined using GPU, but the efficiency depends on the mining difficulty and algorithm.
3. ASIC mining
Application- specific integrated circuits (ASICs) are designed for a single specific purpose. In cryptocurrency, it refers to specialized hardware developed for mining. ASIC mining is efficient but expensive.
Mining competition is fierce. To mine profitably, you need to have competitive mining hardware. ASIC miners have cutting-edge mining technology, and the equipment cost is much higher than CPU or GPU. Also, ASIC technology is advancing so rapidly that older models are no longer profitable, which means that miners need to be replaced frequently. This makes ASIC mining the most expensive method of mining, not counting the cost of electricity.
Go to Binance’s Official Website
4. Mining pool
Since the block reward is awarded to the first successful miner, the probability of finding the correct hash is extremely small. If the miner’s mining power is weak, it is difficult to rely on themselves to find the next block opportunity. Mining pools solve this problem.
Mining pools are groups of miners who pool their resources (hash power) to increase the probability of winning block rewards. When the mining pool successfully finds a block, the miners will split the reward equally according to their individual contribution to the mining pool.
Mining pools can benefit individual miners in terms of hardware and power costs, but their dominance in mining raises concerns about a possible 51% attack on the network.
Conclusion
Cryptocurrency mining is an important force in Bitcoin and other PoW blockchains, and an important factor in maintaining network security and the stable issuance of new coins. Mining has certain advantages and disadvantages, the biggest one being the potential gains from block rewards. However, mining profits are affected by multiple factors such as electricity costs and market prices. Mining is not guaranteed to be profitable, you should do your own research (DYOR) and assess all potential risks before cryptocurrency mining.
Go to Binance’s Official Website
Please check Binance official website or contact the customer support with regard to the latest information and more accurate details.
Binance official website is here.
Please click "Introduction of Binance", if you want to know the details and the company information of Binance.






Comment by jetonwhy
February 16, 2025
Anyone else finding it weird that Deriv only allows deposits through Jeton and not bank transfers? They’ve removed crypto too, so now it’s just cards and Jeton. Kinda frustratin...